饱和脂肪敏感性基因
长期摄入大量饱和脂肪可能会导致肥胖、高血压等问题。对饱和脂肪的敏感性越高,长期摄入大量饱和脂肪后对身体产生这些损害的可能越大。
认知人类基因
renDNA.com
renDNA.com
相关知识
什么是饱和脂肪
脂肪是人体能量的重要来源之一,并可为人体提供必需脂肪酸(只能通过食物摄取而自身不能合成的脂肪酸,如亚油酸),有利于脂溶性维生素的消化吸收。脂肪由甘油和脂肪酸组成,脂肪酸按照化学结构,不含有不饱和键的称为饱和脂肪酸,对应的脂肪即为饱和脂肪。 认知人类基因
过量饱和脂肪导致的问题
常见的食物中,黄油、奶酪、动物油中都含有较多的饱和脂肪。人体需要摄入一定量的饱和脂肪才能保持健康,但是由于饱和脂肪的摄入会导致血液中低密度脂蛋白(更容易粘在血管内壁上,增大血管阻塞的风险)增多,因此摄入过多可能会导致肥胖、高血压、动脉粥样硬化等多种问题。 renDNA.com
建议摄入量
世界卫生组织建议,摄入的脂肪应占总能量的30%以下,并且尽可能使脂肪摄入从饱和脂肪转向不饱和脂肪。饱和脂肪敏感性高的人群,如果有减脂的需求,应该严格控制食物中饱和脂肪酸的含量。 认知人类基因
认知人类基因
检测的基因
中华基因库
renDNA.com
富含饱和脂肪酸的常用食用油脂
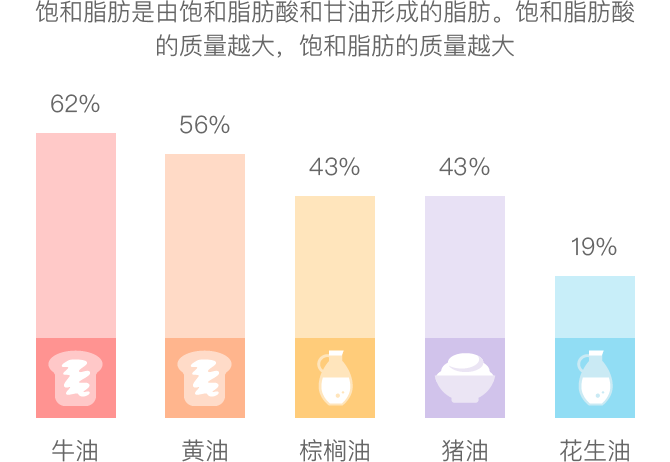 中华基因库
中华基因库
认知人类基因
renDNA.com
参考文献
- Smith C E, Tucker K L, Lee Y C, et al. Low‐density lipoprotein receptor‐related protein 1 variant interacts with saturated fatty acids in puerto ricans[J]. Obesity, 2013, 21(3): 602-608.
- Joffe Y T, van der Merwe L, Collins M, et al. The-308 G/A polymorphism of the tumour necrosis factor-α gene modifies the association between saturated fat intake and serum total cholesterol levels in white South African women[J]. Genes & nutrition, 2011, 6(4): 353-359.
- High fat diet modifies the association of lipoprotein lipase gene polymorphism with high density lipoprotein cholesterol in an Asian Indian population
- Corella D, Peloso G, Arnett D K, et al. APOA2, dietary fat, and body mass index: replication of a gene-diet interaction in 3 independent populations[J]. Archives of internal medicine, 2009, 169(20): 1897-1906.
中华基因库
认知人类基因
附件列表
词条内容仅供参考,如果您需要解决具体问题
(尤其在法律、医学等领域),建议您咨询相关领域专业人士。
如果您认为本词条还有待完善,请 编辑
上一篇 碳水化合物敏感性基因 下一篇 碳水化合物摄入倾向基因
